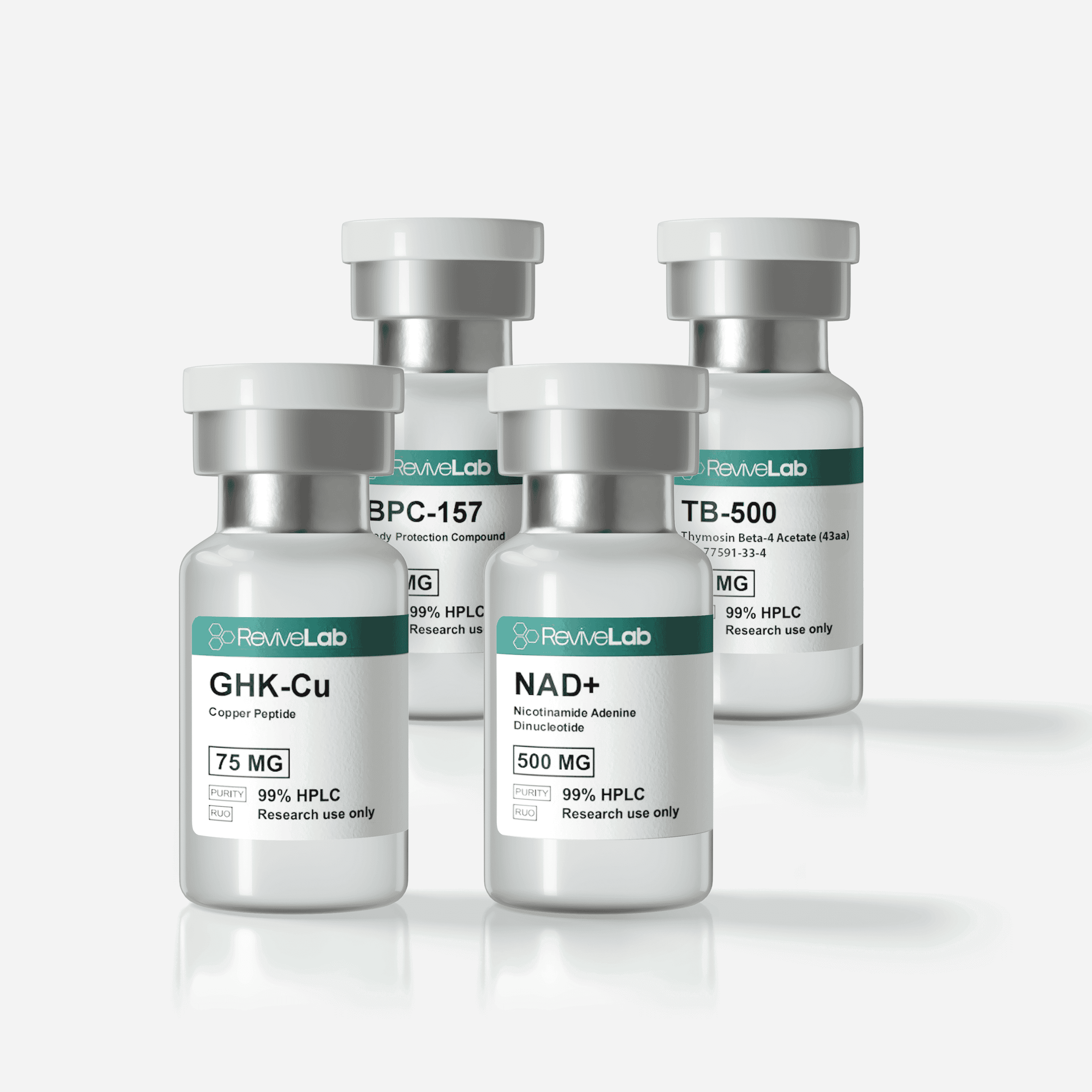
Mitochondrial-Energized Regenerative Stack
Mechanistic Synergy for Research:
The addition of NAD⁺ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) introduces a metabolic enhancement dimension to the peptide trio, reinforcing recovery at the cellular energy and DNA repair level.
- Mitochondrial Energy Support for Regeneration:
NAD⁺ is required for oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production. During active tissue remodeling initiated by BPC-157, TB-500, and GHK-Cu, cellular energy demands are high. NAD⁺ ensures that fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and stem-like cells have adequate metabolic resources to proliferate, migrate, and differentiate. - SIRT1-Mediated Anti-Inflammatory Activity:
NAD⁺ activates sirtuins, especially SIRT1, which deacetylates key transcription factors to suppress pro-inflammatory cytokine production. This effect synergizes with the inflammation-modulating properties of all three peptides, leading to a more controlled and accelerated healing response. - DNA Repair & Longevity Pathway Activation:
NAD⁺ is an essential substrate for PARP enzymes that repair DNA strand breaks. In tissue injury models where oxidative damage is present, NAD⁺ supports cell survival and genomic integrity, enhancing the long-term durability of regenerative outcomes triggered by the peptide stack. - Synergistic Stem Cell Activation:
GHK-Cu and TB-500 mobilize stem cells; NAD⁺ enhances their mitochondrial function and lifespan. This potentiates repair across multiple tissue types, from muscle and skin to nerve and vascular tissues.
Best suited for:
High-demand recovery scenarios, aging tissue models, and studies involving mitochondrial dysfunction or systemic regenerative signaling.
 5-Amino-1MQ
5-Amino-1MQ